Hybrid Manufacture of Aluminium Components
Microstructure of the Substrate and Deposited Material Interface in WAAM
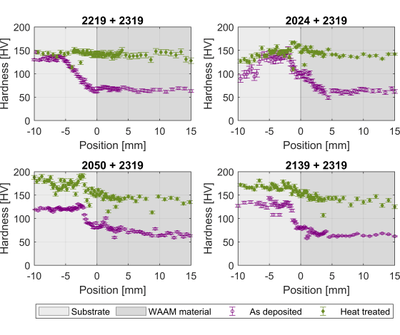
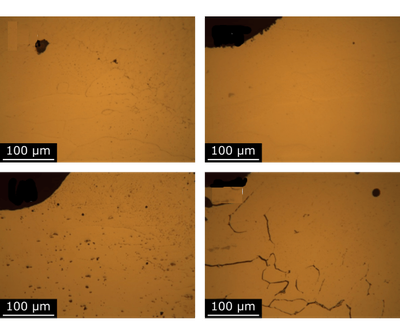
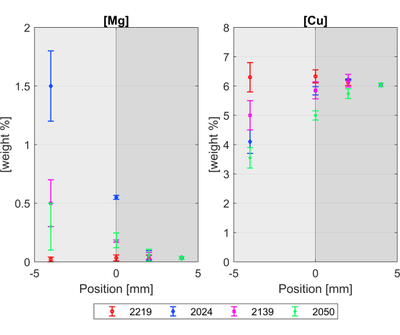
Wire + Arc Additive Manufacture is an Additive Manufacturing process that requires a substrate to initiate the deposition process. In order to reduce material waste, build and lead time, and improve process efficiency, it is desirable to include this substrate in the final part design. This approach is a valid option only if the interface between the substrate and the deposited metal properties conform to the design specifications. The effect of substrate type on the interface microstructure in an aluminium part was investigated. Microstructure and micro-hardness measurements show the effect of substrate alloy and temper on the interface between the substrate and deposited material. Microcracks in the as-deposited condition were only found in one substrate. The deposited material hardness is always lower than the substrate hardness. However, this difference can be minimised by heat treatment and even eliminated when the substrate and wire are made of the same alloy.
E. Eimer, S. Williams, J. Ding, S. Ganguly, and B. Chehab, “Effect of Substrate Alloy Type on the Microstructure of the Substrate and Deposited Material Interface in Aluminium Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing,” Metals (Basel)., vol. 11, no. 6, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.3390/met11060916.
Information
- Research Area:Material Development
-
Investigators:
Eloise Eimer
, Stewart Williams - Publications:https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060916
